OpenAI is an obvious leader in the LLM space, providing great user experience, model quality and performance.
But, how much did recent events affect user confidence?
According to a survey we ran, seems like OpenAI got an average confidence score of just 2.3 out of 5.
Are users contemplating a shift to alternative providers, and if they are, what obstacles are they encountering?
In this blog post we’ll break down the survey's findings and consider what they mean for LLM users and providers.
User Confidence in OpenAI
Although OpenAI is an obvious leader in the LLM space, with GPT-4 still being SOTA compared to other models, recent organizational shifts and uncertainty have impacted user trust.
The results of our survey reveal that a significant 53.1% of respondents indicated they have "Significantly reduced confidence" in OpenAI.
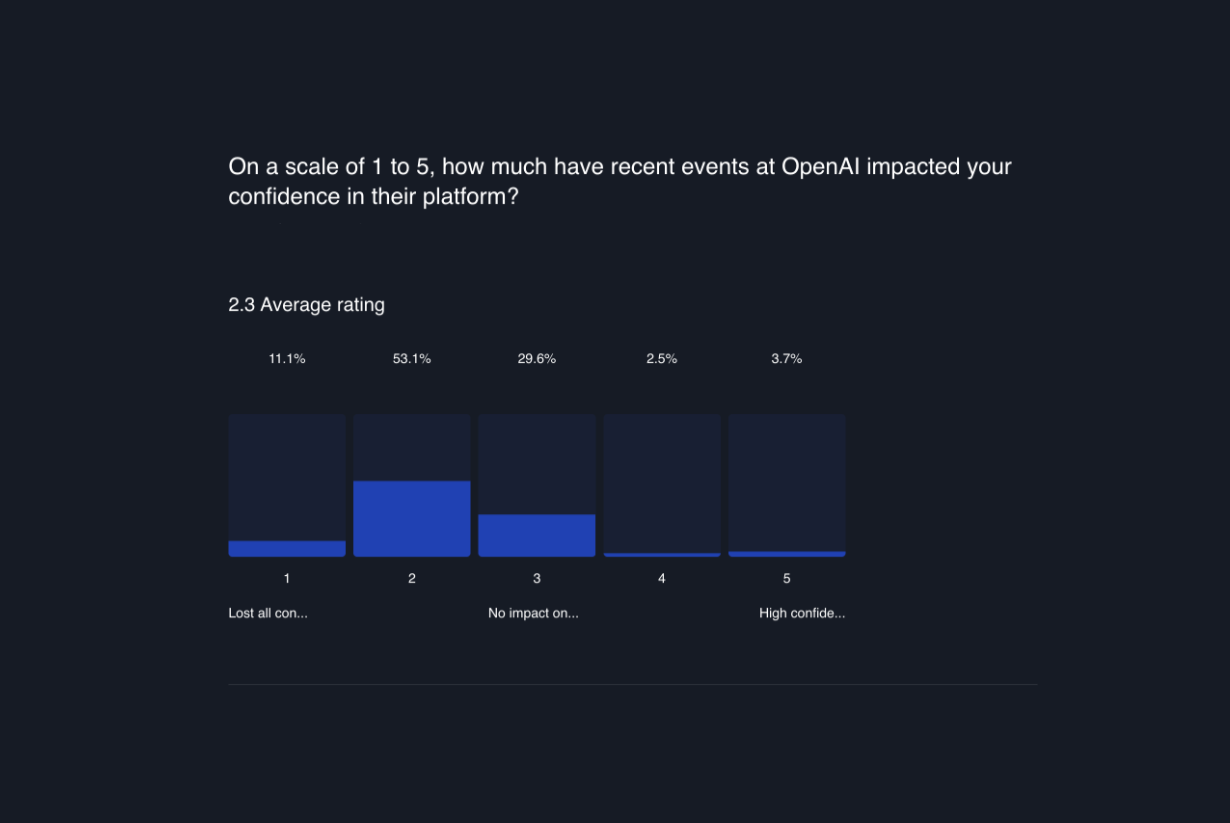
While the leadership at OpenAI has since been reestablished, this period of transition prompted users to reassess their reliance on the platform.
It serves as a reminder of the value of being platform-agnostic, encouraging users to maintain flexibility and openness to various AI providers in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Factors Influencing Users Decisions
When it comes to what's influencing user decisions about staying with or switching from OpenAI, several key factors emerge from the survey.
Survey respondents chose their three most important factors for either continuing to use or moving away from OpenAI. The most commonly selected factors were:
Reliability and Uptime (63%) Accuracy and Performance (54.3%) Cost (40.7%)
This bodes well for OpenAI, as their platform has had high marks on all these factors.
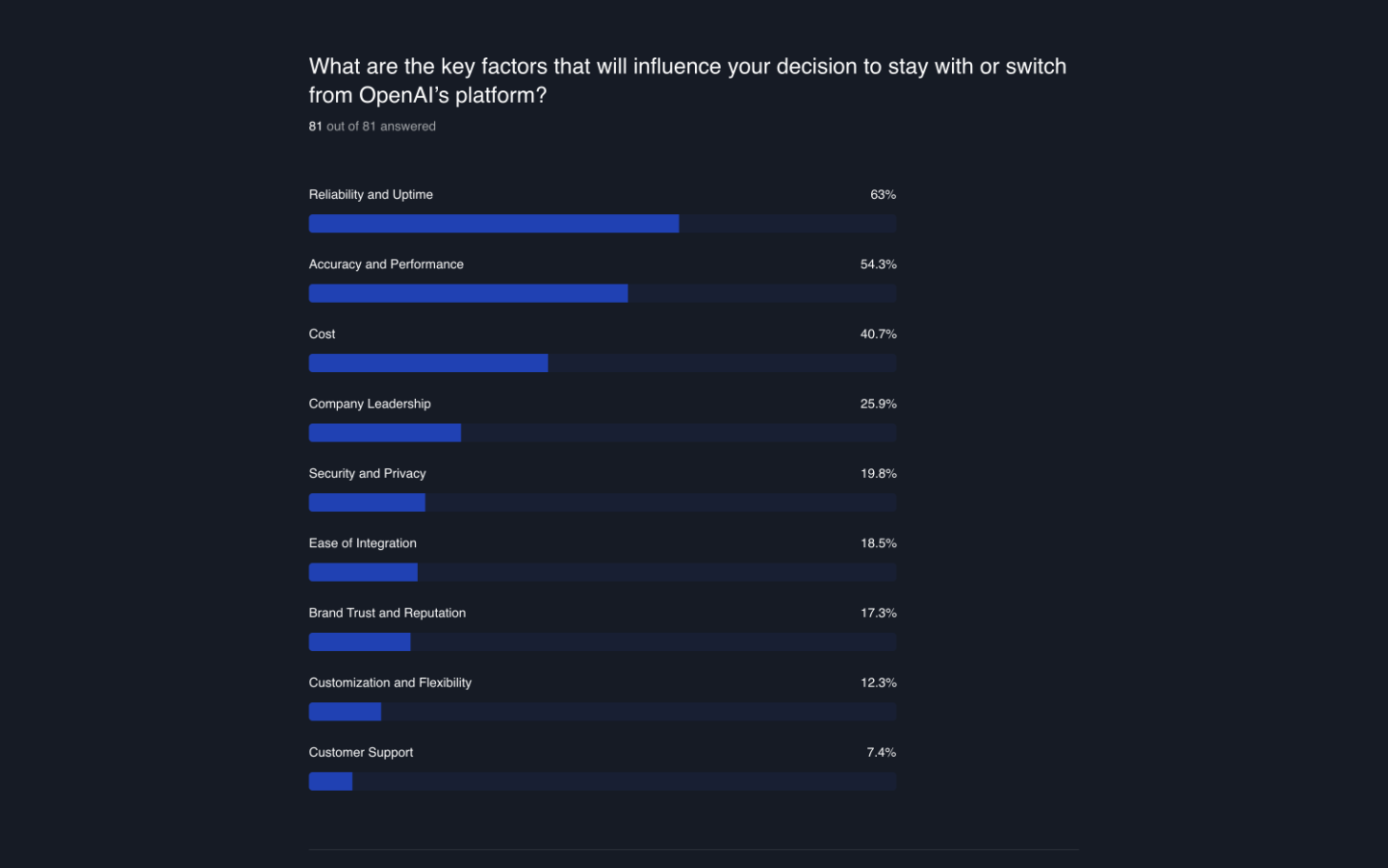
However, Company Leadership (25.9%) comes forth on this list with Security and Privacy (19.8%) right after. The recent leadership upheaval at OpenAI has brought these two aspects to the forefront, underscoring how critical a stable, transparent leadership and robust security measures are in maintaining user trust and loyalty.
Certain factors were ranked lower in priority by users:
Ease of Integration (18.5%) : This lower ranking likely means that users find it easy to integrate OpenAI's services with their systems, and they don't need to do it often. Brand Trust and Reputation (17.3%) : With everything moving so fast, where many providers are relatively new, the focus might be more on technological capabilities than on brand reputation. Customization and Flexibility (12.3%) : Users may feel the existing features of OpenAI meet their needs, making further customization less of a priority. Customer Support (7.4%) : This might be due to users relying more on self-help resources like the OpenAI forum and less on direct support from LLM providers.
Likelihood of Switching to Alternative Providers
The survey also explored how likely OpenAI users are to consider switching to alternative AI providers. Here's what we found:
Unsure (32.1%) : A significant portion of users are undecided about switching. This uncertainty could reflect the rapidly changing AI landscape and the need for more information or time to evaluate alternatives. Somewhat Likely (24.7%) : Over a fifth of the users are considering the possibility of switching, indicating they are keeping an eye on other options but are not fully committed to making a change yet. Very Likely (21%) : A notable group of users are strongly considering alternative options, suggesting they see potential benefits in exploring other AI services. Unlikely (16%) : A smaller segment of users feel unlikely to switch. They may be satisfied with OpenAI's services or find the process of switching too cumbersome. Switching Today (3.7%) : A very small fraction are in the process of switching, indicating immediate dissatisfaction or a strong preference for another provider. Not Switching (2.5%) : Small subset of OpenAI users are definitive about not switching, showing strong loyalty to OpenAI.
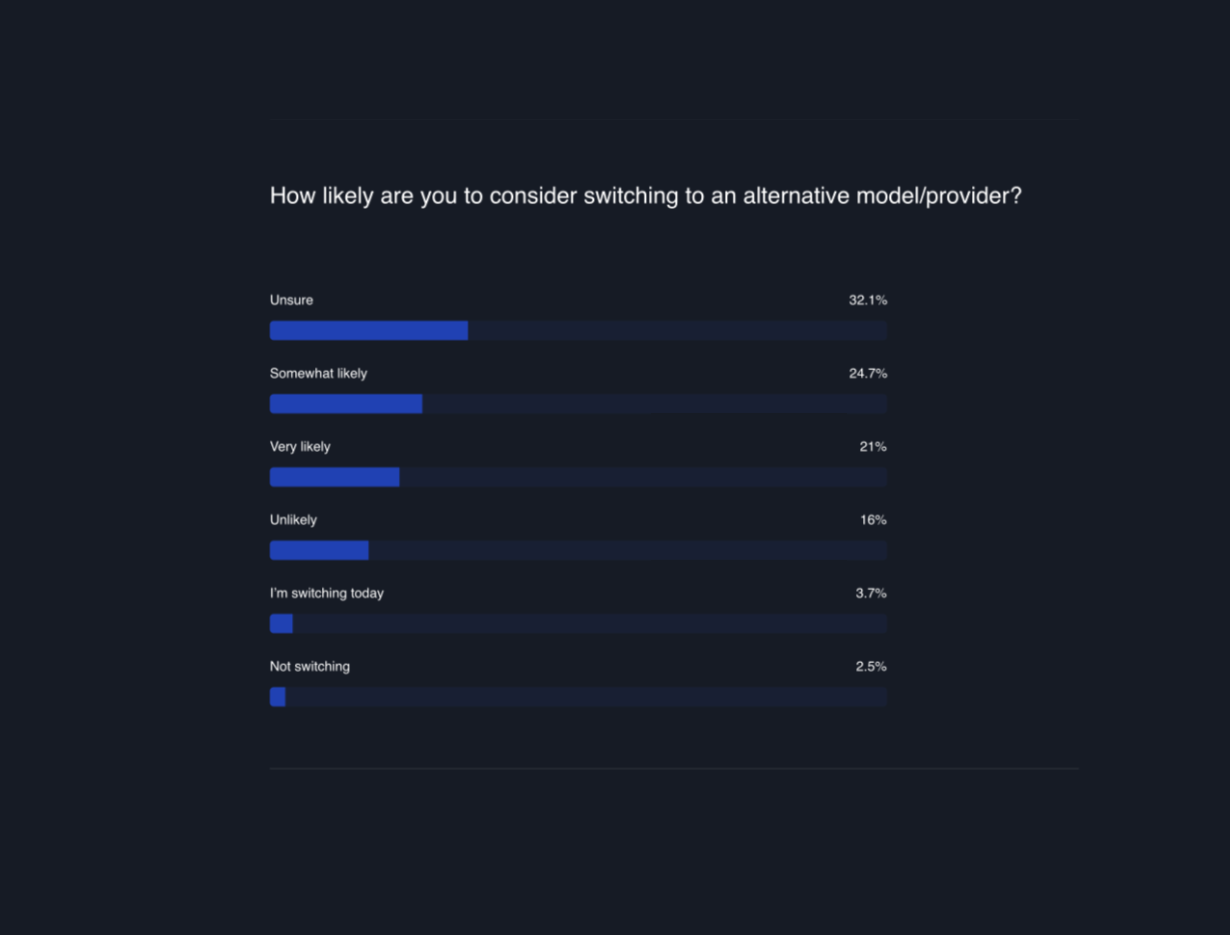
The variety of responses shows a wide spectrum of user opinions about either sticking with or switching from OpenAI, highlighting the dynamic nature of the AI field today.
Preferred Alternatives to OpenAI
The survey also delved into what alternative AI providers OpenAI users are considering.
Here's what we found about their preferences:
Open Source Solutions (60%) : The majority of respondents showed interest in exploring open source AI solutions. Likely due to enhanced security and flexible hosting infrastructure. Also due to cost effectiveness for high usage and for fine-tuned models as we showed in our recent experiment where we reduced cost of a fine-tuned model by >90% by dynamically swapping LoRA weights. Anthropic Models (47.3%) : Many users are looking at LLM solutions from Anthropic, which is emerging as a runner-up in the AI race. During the period of leadership transition at OpenAI, Anthropic capitalized on the opportunity and launched their new Claude 2.1 model , which features function calling capabilities, a feature previously unique to OpenAI models. Major news outlets also reported that more than 100 OpenAI customers reached out to Anthropic. Azure-Hosted OpenAI Models (41.8%) : A significant portion of users are interested in using Azure hosted OpenAI models possibly due to security, latency, and reliability. People may prefer Azure over OpenAI for reasons like data security and compliance requirements. Azure offers private access and more control over data, aligning with specific industry regulations, and provides customization and integration capabilities essential for business operations. AWS Bedrock-Hosted Anthropic models(23.6%): A notable 23.6% of survey respondents are interested in Anthropic models hosted on AWS Bedrock. This preference suggests that users are looking for AI solutions that combine Anthropic's advanced modeling capabilities with the robust, scalable infrastructure provided by AWS Bedrock.
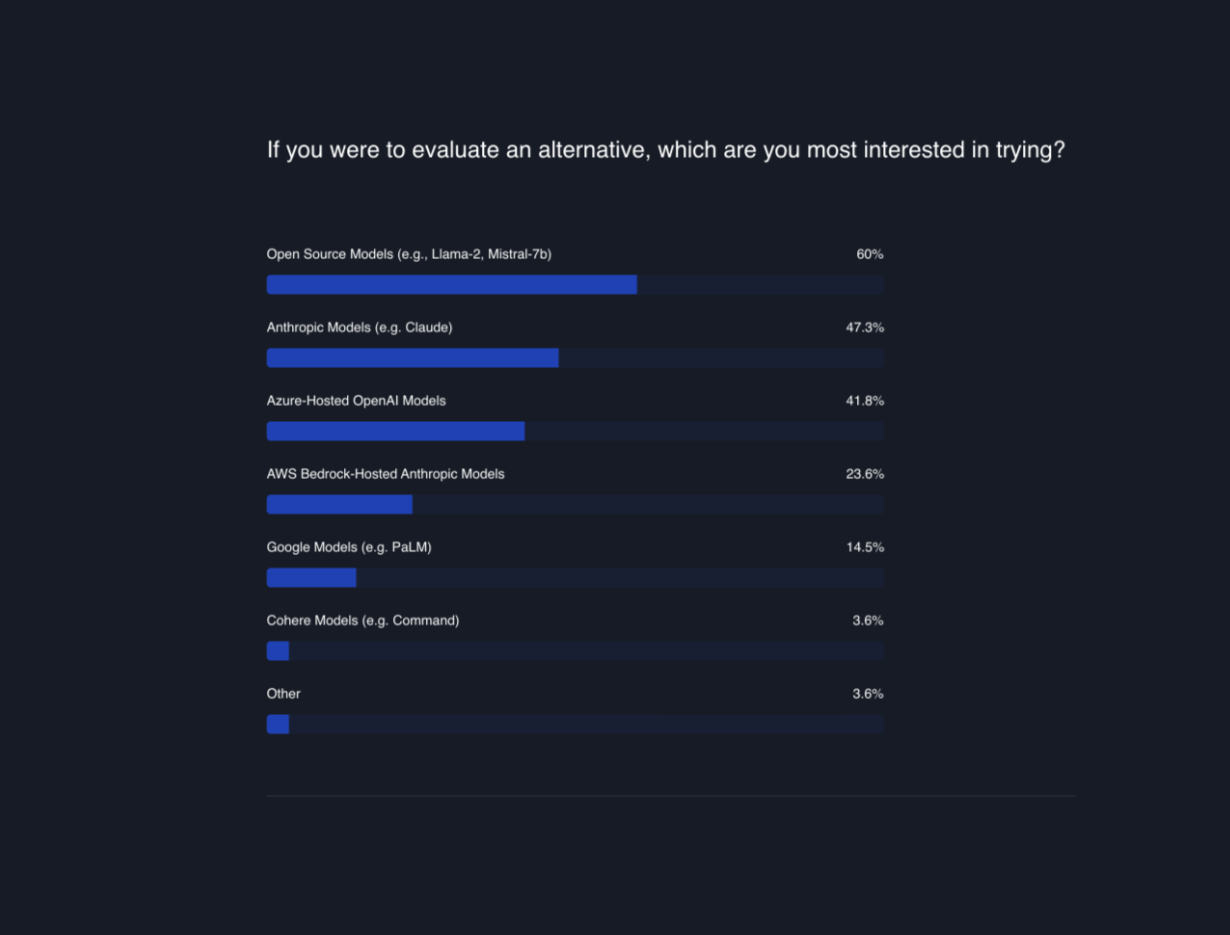
The respondents gave lower preference for Google Models like PaLM (14.5%) , and Cohere Models like Command (3.6%).
Barriers to Switching
While considering alternatives to OpenAI, users face several barriers.
Survey respondents chose their three top challenges when deciding to switch a provider. The most commonly selected barriers were:
Evaluating Model Quality (45.7%) : The primary challenge is assessing the quality of one model against another. Users must determine whether an alternative model meets or exceeds the performance and reliability of OpenAI's offerings for their use-case. Learning Different Prompting Techniques (37%): A major hurdle is mastering the differences in prompting techniques between various models, which can be significantly distinct and require new learning. If you have LLM features in production, updating your whole chain can be unpredictable, and you might need better infra at solving those changes in production. Updating Application Code for New Models(29.6%): The third major challenge involves updating existing application code to be compatible with new models. If you have complex LLM chains in your app, then this involves chaning your whole infra and prompts; which is indeed challenging. Managing the cloud infrastructure needed to host a model (25.9%): The fourth barrier involves the complexities of managing the cloud infrastructure necessary to host an open-source, Azure hosted OpenAI model, or AWS hosted Anthropic model, a task that can be resource-intensive and requires technical expertise.
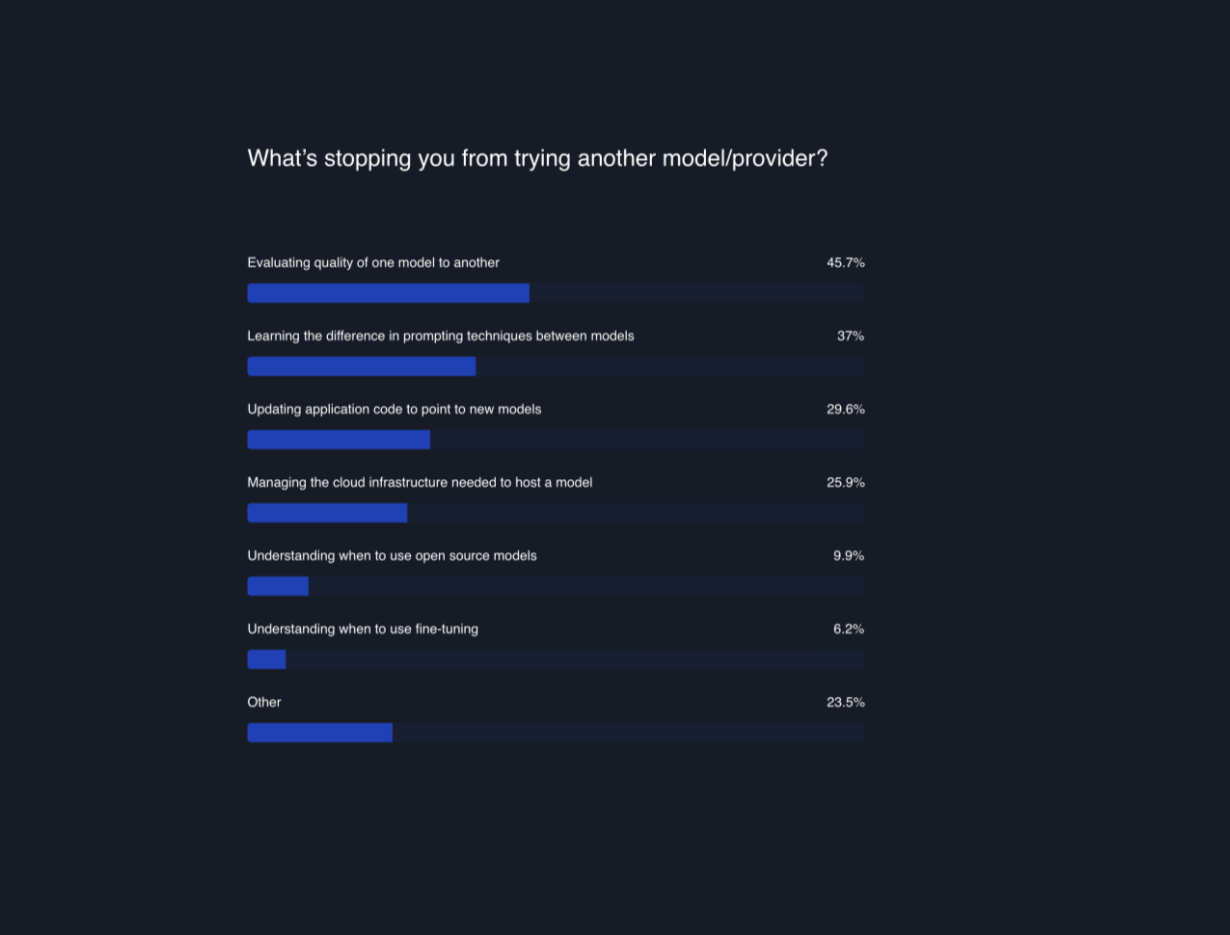
At the bottom of this barrier list is the “ Understanding when to use open source models (9.9%) ” and “ Understanding when to use fine-tuning (6.2%) ”, indicating that while these issues are less prevalent, they still exist as notable considerations for users.
Conclusion
The survey on user sentiment towards OpenAI and potential alternatives reveals a complex landscape influenced by various factors.
Here's a summary of the key points:
User Confidence : Recent leadership changes and other factors have led to a significant reduction in user confidence in OpenAI.
Top Influencing Factors : Reliability, accuracy, and cost are the top factors impacting user decisions about staying with or switching from OpenAI.
Alternatives Considered : Users are exploring options like open-source solutions, Anthropic models, and Azure-hosted OpenAI models, reflecting a diverse range of interests and needs.
Barriers to Switching : Key challenges include evaluating model quality, learning different prompting techniques, and managing cloud infrastructure.
How Can Vellum Help
We understand that handling Large Language Models (LLMs), especially when they're in production, can be challenging. And that’s why we’re building Vellum.
With Vellum you can iterate on different prompts with various providers, whether it's major providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, open source models like LlaMa and Mistral, or those hosted on Azure or AWS. No need to overhaul your setup; Vellum hosts these models for you.
Plus, you can evaluate your LLM outputs at every step of your chain , and control versions easily, all without major code changes on your end.
Let us know if you need assistance with this by requesting a demo on this link , or contacting us directly on support@vellum.ai .
Survey Overview
We conducted this survey with a clear objective: to understand how recent developments at OpenAI have impacted user confidence in their platform. Specifically, we sought to explore the factors influencing users' decisions to stay with or switch from OpenAI, as well as their interest in alternative AI models.
A group of 81 participants, all actively engaged with OpenAI, generously shared their insights. The survey was conducted over a period of one week, from November 20th to November 26th.
The results we present are aimed at providing the community and our customers with a clearer understanding of the current AI landscape and the prevailing sentiments within it.
*Given that our survey was completed by 81 individuals, it's important to note that while these responses provide valuable insights, they represent a limited sample of the broader user base. Therefore, these findings, should be viewed as indicative rather than definitive of the general market sentiment.
Table of Contents
User Confidence in OpenAI Factors Influencing User Decisions Likelihood of Switching to Alternative Providers Preferred Alternatives to OpenAI Barriers to Switching Conclusion How can Vellum help Survey Overview